
Density of air is 0.85 kg/m3 and viscosity is 1.47 x 10-5 kg/m.s. A small spherical particle (diameter = 75x10-6 m) is falling through air from a high elevation. A small spherical particle (diameter = 75x10-6 m) is falling through air from a high.Ģ.

QUESTION 10 Calculate the terminal velocity a spherical rain drop, diameter. What is the drag force at 97.4 MPH for a Hummer H2? (Drag area for Hummer is 2.44 m² and look up Table 5.2 chap 5 for the drag coefficient) Express your answer in N with 3 significant figures.
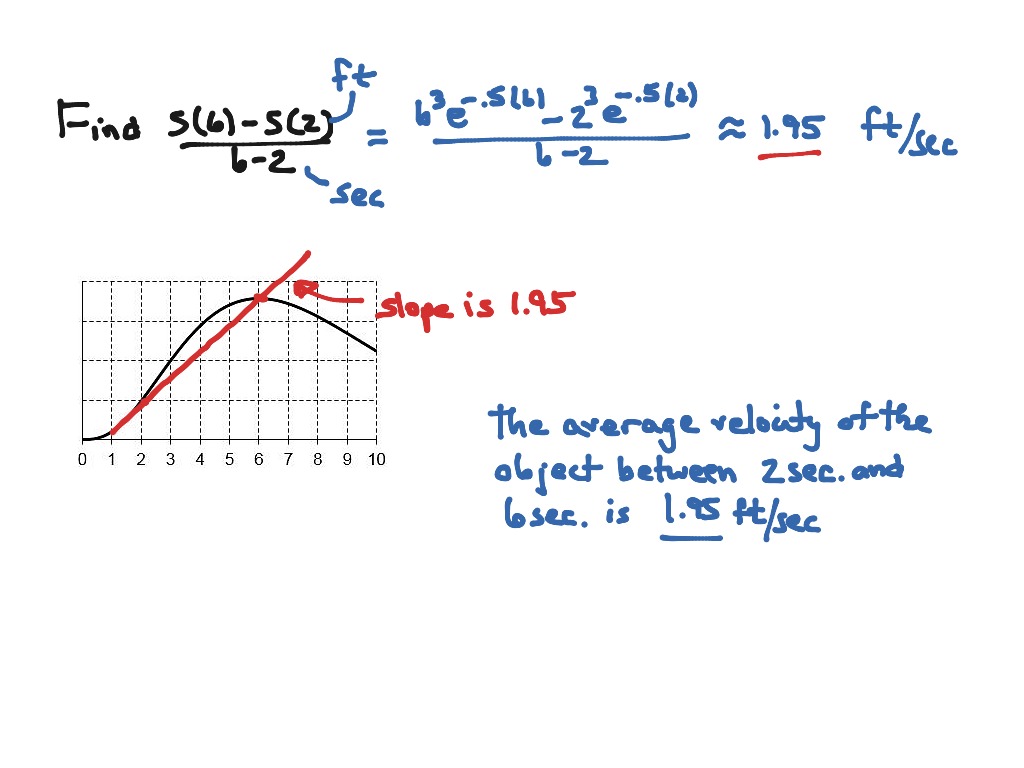
Calculate the velocity of a spherical raindrop plus#
QUESTION 9 To maintain a constant speed, the force provided by a car's engine must equal the drag force plus the force of friction of the road (the rolling resistance).

However, research has found the shape of a raindrop to be rather spherical or slightly flattened on the bottom by airflow like a hamburger bun. It is often depicted as pointy and lopsided.

A common misconception is the shape of the raindrop. The magnitude of the terminal velocity of an object is also affected by its orientation. At this point, a raindrop experiences no further acceleration and therefore falls at a constant velocity. The combination of these two forces causes a raindrop to reach a terminal velocity when the drag force is approximately equal to the weight of the raindrop. Usually, air resistance that comes in contact with the water molecules as they fall causes the drag. As gravity increases the speed of the raindrop in its descent, drag retards the downward acceleration of the raindrop. A stationary raindrop initially experiences an acceleration due to gravity of 9.8 m/s 2, as would any falling body. When a raindrop falls to the surface of the Earth, it is acted on by two main forces, gravity and drag. Of course all raindrops vary in size due to the strength of a specific rainstorm, but this is considered a reasonable value of a typical raindrop. The average size of a raindrop is 6 millimeters in diameter, about the size of a housefly. Once enough water has evaporated, it is then released in the form of droplets of rain back to the surface of the Earth. The water that forms these clouds is frozen and vaporized. It is part of the hydrologic cycle that begins when water evaporates and forms clouds in the atmosphere. Rain is the liquid form of precipitation on Earth. Drizzle drops (less than 0.5 mm across, i.e., salt-grain size) fall at 2 meters per second (4.5 mph)." "At sea level, a large raindrop about 5 millimeters across (house-fly size) falls at the rate of 9 meters per second (20 miles per hour). Falling raindrops hit 5 to 20 mph speeds. Raindrop Size, Shape, and Falling Speed . Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences (May 1976): 851-864. Terminal Velocity and Shape of Cloud and Precipitation Drops . "Large raindrops, up to six millimeters in diameter, have terminal velocities of about 10 metres per second and so may cause considerable compaction and erosion of the soil by their force of impact."īeard, K.V. "Climate." Encyclopedia Britannica.2007, Encyclopedia Britannica Online. "A large drop of about 5 mm (3/16 in.) diameter reaches a maximum speed of about 9 m/sec."


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
